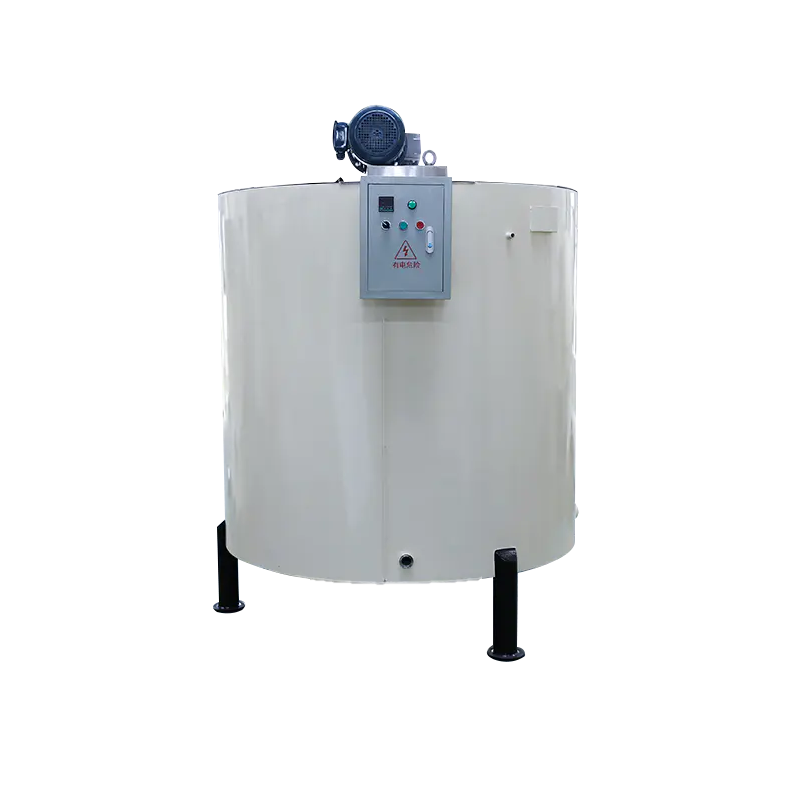
In chocolate production, maintaining consistent quality throughout the manufacturing process is essential. One of the most critical stages is the storage and handling of melted chocolate prior to its use in molding, enrobing, or other downstream processes. The Chocolate Holding Tank serves as the central vessel for storing and regulating chocolate temperature before further processing. Its design and operation directly influence product consistency, texture, appearance, and overall production efficiency.
Temperature control in a chocolate holding tank is not merely a convenience—it is a decisive factor that affects chocolate stability, viscosity, and shelf life.
The Role of Chocolate Holding Tank in Production
A Chocolate Holding Tank is specifically engineered to hold tempered chocolate at a controlled temperature, ensuring it remains in a stable, fluid state suitable for processing. Unlike storage tanks for other liquids, chocolate presents unique challenges due to its susceptibility to crystallization, separation of cocoa butter, and viscosity changes when temperature fluctuates.
Key operational functions of a chocolate holding tank include:
- Maintaining uniform heat distribution to prevent localized cooling or overheating
- Providing a stable environment for chocolate to retain its creamy texture and glossy finish
- Supporting continuous production lines by serving as a buffer between melting and molding or enrobing
The selection and operation of chocolate holding tanks directly affect production efficiency, product quality, and operational costs. Any lapse in temperature control can lead to defects, including fat bloom, uneven texture, or crystallization.
Importance of Temperature Control
Chocolate Viscosity and Flow
One of the most critical aspects of chocolate handling is maintaining proper viscosity. Chocolate that is too cool can become too thick to pump or deposit correctly, leading to production slowdowns. Conversely, chocolate that is too hot may become too fluid, resulting in poor coating performance or air incorporation.
A properly controlled Chocolate Holding Tank ensures chocolate remains at an optimal working viscosity, facilitating smooth transfer to downstream equipment such as enrobers, molds, or tempering systems.
Prevention of Crystallization
Chocolate is highly sensitive to temperature changes. Fluctuations can trigger premature cocoa butter crystallization, resulting in undesirable textures and surface defects. By maintaining a stable temperature, chocolate holding tanks prevent these crystallization issues and ensure product consistency.
Table 1 illustrates the temperature ranges suitable for different types of chocolate in holding tanks:
| Chocolate Type |
Optimal Holding Temperature (°C) |
Viscosity Notes |
| Dark Chocolate |
45–50 |
Medium viscosity, stable flow |
| Milk Chocolate |
40–45 |
Slightly lower viscosity |
| White Chocolate |
38–43 |
Highly sensitive to overheating |
Maintaining these ranges prevents structural inconsistencies and ensures chocolate remains ready for processing without additional tempering.
Quality and Appearance
Temperature directly influences chocolate’s surface finish, gloss, and mouthfeel. Improper control can lead to bloom, streaks, or dull appearance, affecting the visual and sensory appeal of the final product.
A chocolate holding tank with precise heating and agitation ensures that cocoa butter remains uniformly distributed, avoiding separation and fat migration that could compromise both taste and presentation.
Shelf Life and Stability
Holding chocolate at consistent temperatures extends its stability by reducing the risk of premature crystallization or degradation. Manufacturers benefit from reduced waste, fewer rejects, and predictable production cycles. The Chocolate Holding Tank effectively acts as a thermal buffer, allowing for controlled storage even when production schedules fluctuate.
Features Supporting Temperature Control
Modern chocolate holding tanks integrate multiple design elements and technologies to maintain precise temperature:
- Heating Jackets and Coils: External or internal heating systems ensure uniform temperature distribution throughout the tank.
- Agitation Mechanisms: Gentle stirring prevents localized cooling or overheating, maintaining consistent fluidity.
- Insulation: High-quality insulation minimizes heat loss, reducing energy consumption and maintaining stable conditions.
- Digital Temperature Controllers: Programmable controllers with feedback loops provide accurate, real-time monitoring and regulation.
- Safety Cutoffs: Automatic shutoff mechanisms prevent overheating and maintain operational safety.
Table 2 summarizes common features and their impact on temperature stability:
| Feature |
Purpose |
Benefit |
| Heating Jackets |
Uniform heat distribution |
Prevents hot/cold spots |
| Agitation System |
Maintains consistent flow |
Avoids separation and uneven crystallization |
| Insulation |
Reduces heat loss |
Improves energy efficiency |
| Digital Controller |
Precise temperature monitoring |
Enables stable holding conditions |
| Safety Cutoffs |
Prevent overheating |
Protects chocolate quality and equipment |
Operational Considerations
Chocolate Type and Composition
Different chocolate types (dark, milk, white) have distinct melting points and thermal sensitivities. Chocolate Holding Tank operators must adjust temperatures and agitation to match the specific chocolate composition, taking into account cocoa solids, sugar content, and added inclusions.
Agitation and Flow Dynamics
Continuous or intermittent agitation ensures uniform temperature and prevents sedimentation or separation of cocoa butter and solids. Flow dynamics within the tank must be carefully controlled to avoid air incorporation, which can affect texture and shine.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning is essential to prevent residue buildup, microbial growth, and flavor contamination. Maintaining precise temperature also assists in cleaning, as residual chocolate softens for easier removal without damaging the tank surfaces.
Integration With Production Line
For high-volume operations, the Chocolate Holding Tank often interfaces with tempering machines, molding lines, and enrobing equipment. Temperature fluctuations can propagate downstream, causing defects in the final product. Coordinated control ensures smooth production continuity.
Benefits of Effective Temperature Control
Effective temperature control in a chocolate holding tank provides several tangible benefits:
- Consistent chocolate quality: Prevents defects like bloom, streaks, or uneven texture.
- Operational efficiency: Reduces downtime and facilitates continuous production.
- Extended shelf life: Stable temperatures slow degradation and crystallization.
- Energy savings: Well-insulated tanks with optimized heating reduce energy consumption.
- Safety and hygiene: Precise control prevents overheating, reduces contamination risk, and supports clean-in-place processes.
Common Challenges
Despite advanced technology, manufacturers may encounter issues related to temperature control:
- Uneven heat distribution in large tanks
- Improper agitation leading to cocoa butter separation
- Inaccurate temperature sensors or delayed feedback
- Energy inefficiencies in poorly insulated tanks
Addressing these challenges requires careful design, operator training, and routine monitoring.
Advanced Considerations
Modern Chocolate Holding Tank systems increasingly incorporate:
- Automated monitoring and alarm systems to detect temperature deviations
- Variable-speed agitators to adapt to different chocolate viscosities
- Integrated sensors for viscosity, flow, and thermal consistency
These enhancements allow manufacturers to achieve precise temperature regulation while maintaining production flexibility.
Conclusion
Temperature control is critical in a chocolate holding tank because it directly impacts viscosity, crystallization, appearance, shelf life, and production efficiency. By maintaining precise and uniform temperatures, manufacturers ensure consistent chocolate quality, reduce waste, and optimize operational performance. Modern tank designs, incorporating heating jackets, agitation, insulation, and digital controllers, enable effective temperature management, addressing the unique challenges presented by chocolate’s thermal sensitivity.
FAQ
Q1: What is the recommended temperature for storing dark chocolate in a holding tank?
A1: The optimal range is 45–50°C, ensuring medium viscosity and stable flow for processing.
Q2: How often should a chocolate holding tank be cleaned?
A2: Cleaning frequency depends on production cycles, but tanks should be cleaned after each batch or at least daily to prevent residue buildup and contamination.
Q3: Can one chocolate holding tank handle multiple types of chocolate simultaneously?
A3: While possible, it is generally recommended to dedicate separate tanks for dark, milk, and white chocolate due to different thermal sensitivities.
Q4: What are the consequences of poor temperature control in chocolate holding tanks?
A4: Poor control can lead to crystallization, fat bloom, uneven texture, inconsistent viscosity, and compromised product quality.
Q5: How does agitation affect temperature control in chocolate holding tanks?
A5: Agitation ensures uniform heat distribution and prevents separation, maintaining consistent chocolate viscosity and quality.
References
- Beckett, S.T., Industrial Chocolate Manufacture and Use, Springer, 2019.
- Minifie, B.W., Chocolate, Cocoa and Confectionery: Science and Technology, Springer, 2012.
- Halm, M., Chocolate Technology and Applications, Wiley-Blackwell, 2017.


 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Français
Français عربى
عربى